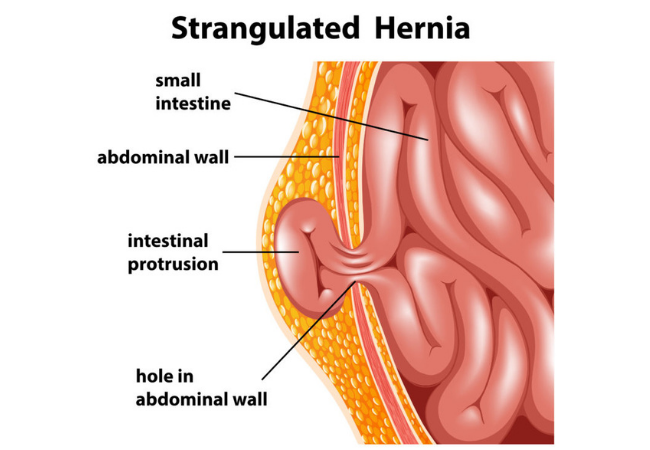
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. It can happen in the abdomen, groin, or belly button area.
Hernia surgery can be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, which involves small incisions and quicker recovery.
Laparoscopic hernia surgery involves smaller incisions, less pain, a shorter hospital stay, and quicker recovery time compared to open surgery.
Yes, hernia surgery is generally safe, with a high success rate. However, like any surgery, it carries some risks, which your surgeon will discuss with you beforehand.
Recovery typically takes 1-2 weeks for laparoscopic surgery and 4-6 weeks for open surgery, depending on the individual’s health and the surgery's complexity.
Though rare, hernias can recur if the surgical repair doesn’t fully heal or if a person engages in strenuous activities too soon. Following post-surgery care instructions is crucial.
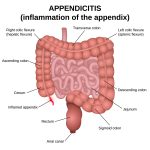
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small organ attached to the large intestine. It can cause severe pain and requires prompt surgery (appendectomy) to remove the appendix.
Appendicitis is usually treated by removing the appendix through laparoscopic surgery, which uses small incisions, or open surgery in more severe cases.
Complications are rare but can include infection, bleeding, or injury to surrounding organs. These risks will be carefully managed by your surgeon.
Laparoscopic appendectomy typically requires 1-2 weeks of recovery, while open surgery may take longer, up to 4-6 weeks.
No, once the appendix is removed, appendicitis cannot recur.
Follow your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, which may include limiting physical activity, taking prescribed medications, and attending follow-up appointments.
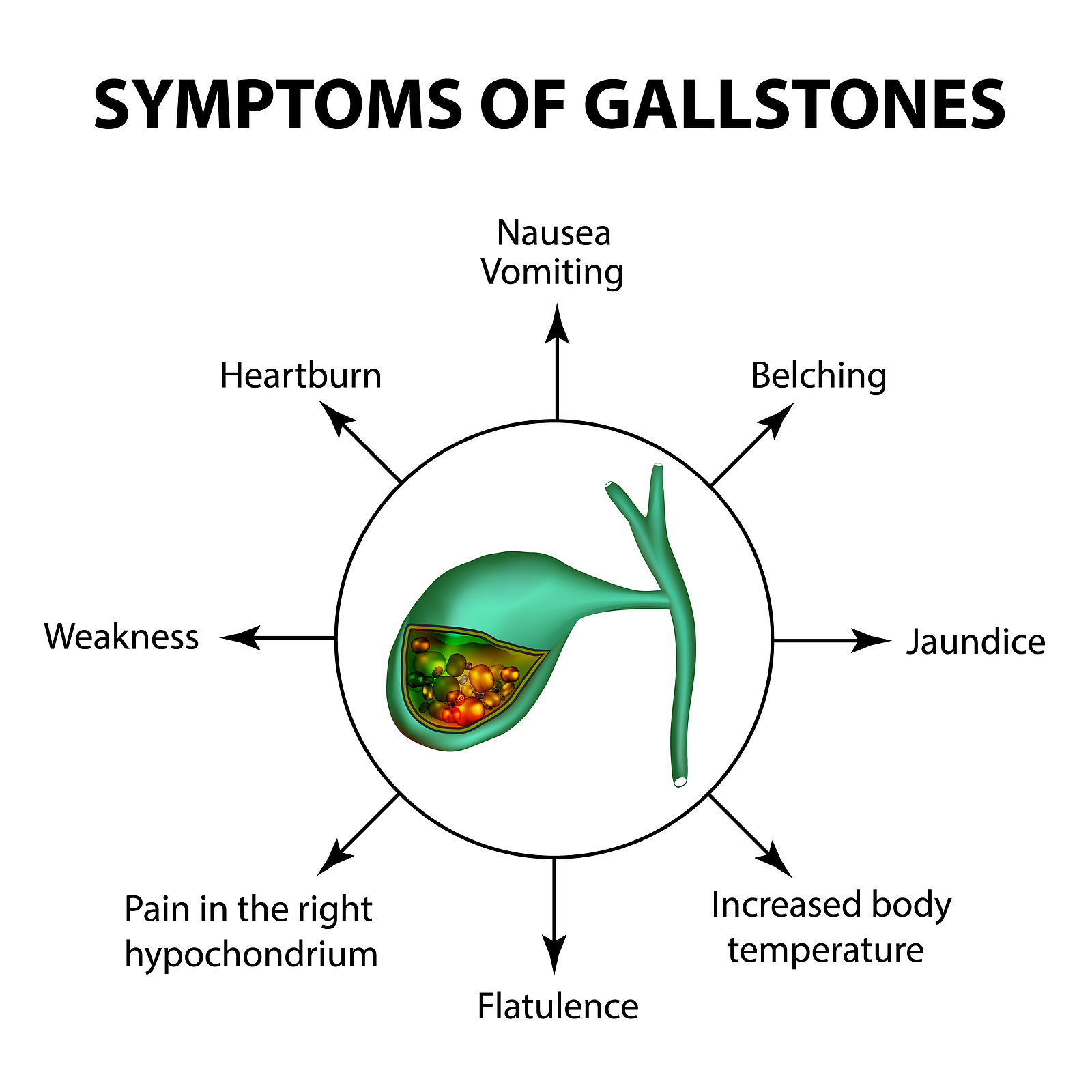
Cholecystitis is the inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones. This can lead to severe pain and requires surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
The gallbladder may need to be removed if it is inflamed, infected, or has gallstones that cause pain or complications. The surgery helps to prevent further issues.
Gallbladder removal is most commonly done through laparoscopic surgery, involving small incisions. This method offers faster recovery and less pain than open surgery.
Most people live a normal life without a gallbladder. Your liver will still produce bile to help digest food, though you may need to adjust your diet to avoid fatty foods initially.
Yes, cholecystectomy is a common and safe procedure with a low risk of complications when performed by an experienced surgeon.
Recovery usually takes 1-2 weeks for laparoscopic surgery, with a gradual return to normal activities.
Dr.Sanjitha is very helpful and polite she responds very quickly to any issues related and I had got operated and was healed very quickly nice hand thank u mam fr all ur co operation 😊👌
She is a very kind doctor who listens to your issues and queries and Informs you of the options available to you in detail. She is available for any questions we can have and it is highly appreciated. she is willing to spend time to explain the procedures as well as comfort the patient. Duly recommend her services.
Very good doctor, she helped me with my problem which I didn't know what it was - I went to ortho doctor thinking some spine issue but madam told it's pilonidal sinus and did surgery for me. Now I am back to normal and painfree. Thankyou madam.
Dr Sanjitha was kind and approachable throughout the process of my treatment ... be it consultation , pre /post op check ups and follow ups . Thankyou mam . Please keep up your good work and continue to inspire all your fellow doctors.
Appreciate the thoroughness of the examination. Dr.Sanjitha took the time to explain everything in detail. I want to express my heartfelt gratitude for your unwavering dedication and compassionate care. Thank you for being an exceptional doctor.
Dr.Sanjita is very kind and an energy booster, I would say. She always give a positive energy and we don't even feel like we are sick, and responds immediately even for messages. I have done hemorrhoid surgery recently. I was totally scared to go to a doctor and do the surgery. But from the first consultation itself I got a very good confidence from the way doctor treated me and explained the procedure. I would really recommend her. Thank you Doctor 🙏
Click Here to View Google Map

Website Designed by HappiMed